数据更新->视图更新,是现代前端框架的根本目的。原生js和jquery在项目开发中,代码逻辑中穿插大量dom操作,会给项目的开发,维护,稳定运行带来很大的困境。所以在我看来,现代前端框架所要解决的核心问题,就是数据和视图分离(代码逻辑中的分离),或者说是数据和视图的绑定(所得既所见),从前我们处理完数据需要手动去更新dom操作,而有了前端框架,我们便可以-所得既所见,当我们根据业务逻辑更改了数据,不需要我们手动操作dom节点,这些现代前端框架会去帮我们完成刷新,所以在我看来,现代前端框架得核心功能只有一个,就是那加粗的五个字,**所得既所见。**至于其它的,什么生命周期,副作用,状态管理, ref等等,或是什么fiber架构,diff算法,concurrent模式,状态队列等等,都只是为了完成这个目标,或者更好的完成这个目标。在这一点上,react也好, vue也好,都是如此。只不过两者在具体实现上采用的策略存在差异,如数据更新触发视图更新,vue采用getter, setter侦听来实现数据到视图的双向绑定,自动更新,而react则通过手动调用setState来触发视图更新,所得既所见的目的相同,只是实现策略不同。 综上所述,数据更新->试图更新,所得既所见。就是我所认为的现代前端框架的核心,而其它的一切皆围绕于此。所以关于react的故事,我想必须从useState开始。
一、在使用是我们从react中导出useState使用,所以找到源码/packages/react/src/react.js为使用该库的入口文件。
找到导出的setState,看他是从哪里引入的,你会发现导出的setState来自源码/packages/react/src/reactHook.js
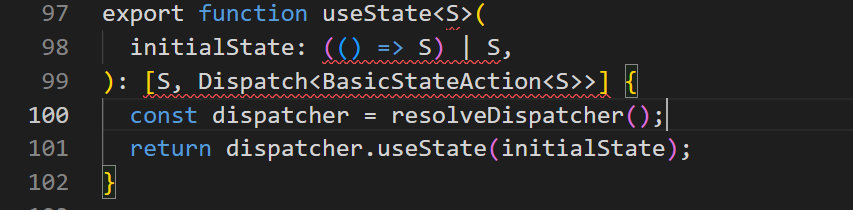 resolveDispatcher实现如下:
resolveDispatcher实现如下:
 结合这两段代码当我们在项目中使用useState时:const [state, setState] = useState(initialState);
就相当于 const [state, setState] = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current.useState(initialState)。
结合这两段代码当我们在项目中使用useState时:const [state, setState] = useState(initialState);
就相当于 const [state, setState] = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current.useState(initialState)。
二、ReactCurrentDispatcher又是什么?
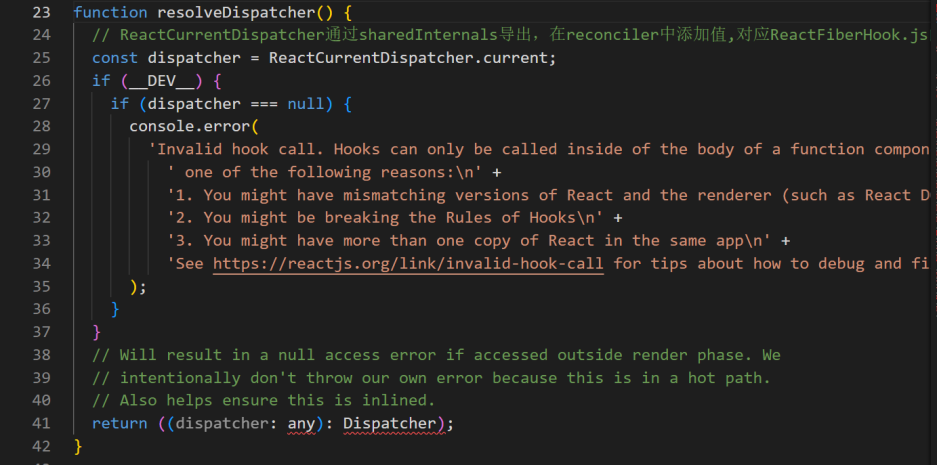
变量定义在/packages/react/src/ReactCurrentDispatcher.js,代码如下。
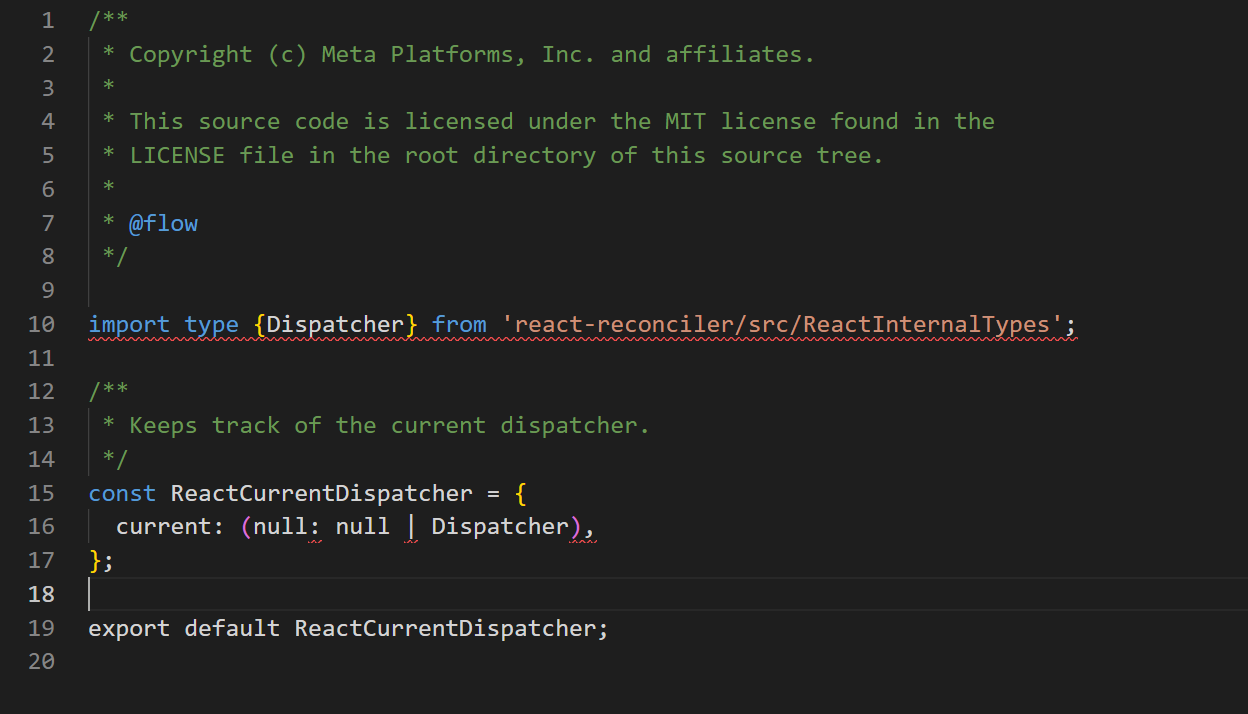 如你所见,整个源文件只有几行,这里只进行了变量定义。ReactCurrentDispatcher的current属性又是在哪里赋值的呢?直接讲答案:packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js。
ReactCurrentDispatcher在/packages/react/src/ReactSharedInternals.js共享给其它文件夹。源码的/packages/shared/ReactSharedInternals.js收集这些全局共享变量。这些全局共享变量可以通过/packages/shared/ReactSharedInternals.js引入,在源码全局范围内修改或使用。
如你所见,整个源文件只有几行,这里只进行了变量定义。ReactCurrentDispatcher的current属性又是在哪里赋值的呢?直接讲答案:packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js。
ReactCurrentDispatcher在/packages/react/src/ReactSharedInternals.js共享给其它文件夹。源码的/packages/shared/ReactSharedInternals.js收集这些全局共享变量。这些全局共享变量可以通过/packages/shared/ReactSharedInternals.js引入,在源码全局范围内修改或使用。
三、所以讲视线转到packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js中,看ReactCurrentDispatcher.current是如何赋值的。
在ReactFiberHooks.js源码中找到renderWithHooks函数,你可看到如下代码:
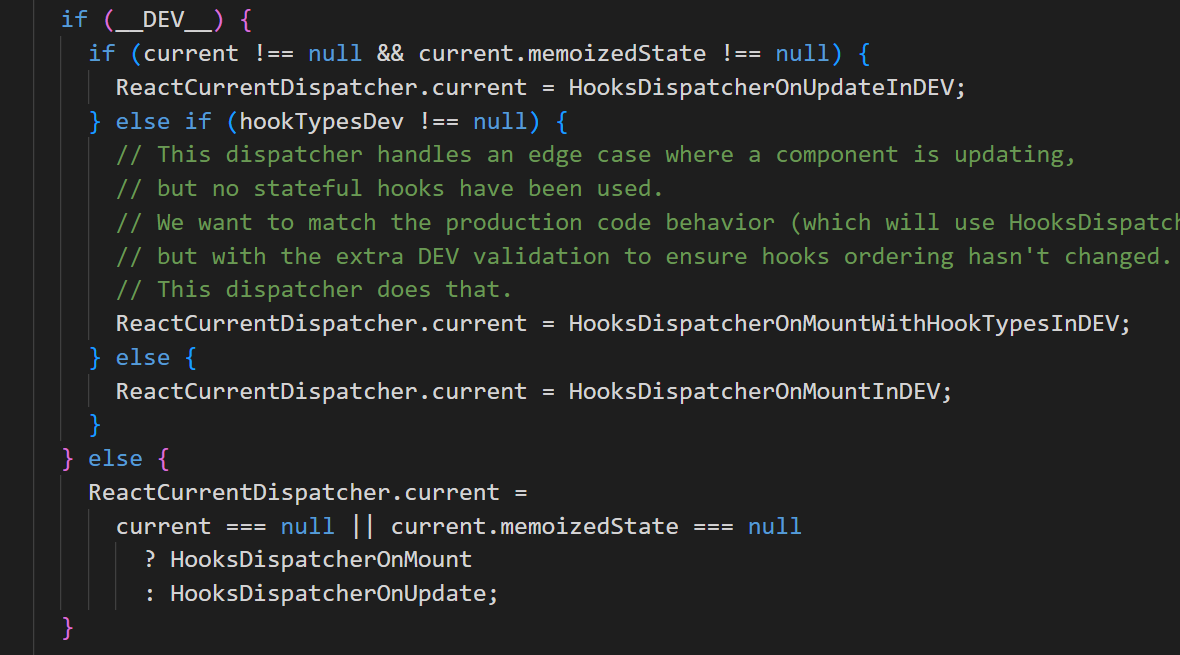 这里你可以看到ReactCurrentDispatcher.current是如何赋值的。外层分支区分生产开发环境,内层分支主要分两种情况更新Update,挂在Mount。会根据renderWithHooks的调用时机选择不同的赋值。我们先以挂载mount为例,看看HooksDispatcherOnMount,到底是个什么。
这里你可以看到ReactCurrentDispatcher.current是如何赋值的。外层分支区分生产开发环境,内层分支主要分两种情况更新Update,挂在Mount。会根据renderWithHooks的调用时机选择不同的赋值。我们先以挂载mount为例,看看HooksDispatcherOnMount,到底是个什么。
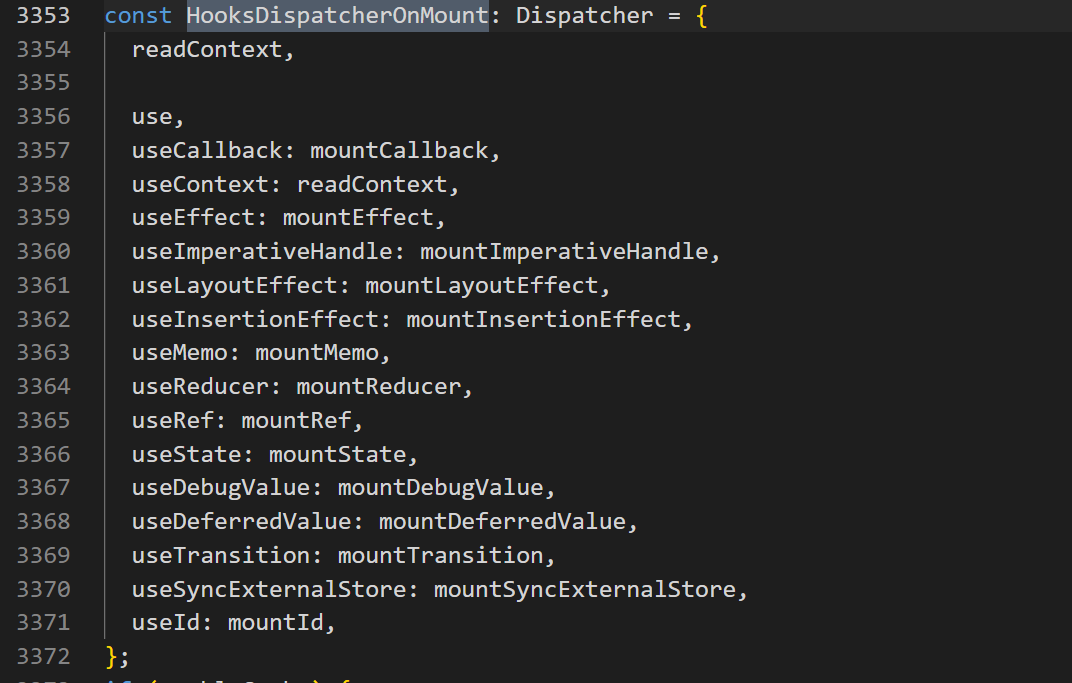 这个对象便是ReactCurrentDispatcher.current在挂载阶段的值了。那么它的useState就对应mountState变量。
所以(一)中所讲:”在项目中使用useState时:const [state, setState] = useState(initialState);
就相当于 const [state, setState] = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current.useState(initialState)。“
在这里,又等价于const [state, setState] = mountState(initialState);
这个对象便是ReactCurrentDispatcher.current在挂载阶段的值了。那么它的useState就对应mountState变量。
所以(一)中所讲:”在项目中使用useState时:const [state, setState] = useState(initialState);
就相当于 const [state, setState] = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current.useState(initialState)。“
在这里,又等价于const [state, setState] = mountState(initialState);
四、我们继续看mountState是什么?
mountState的实现仍位于packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js中。
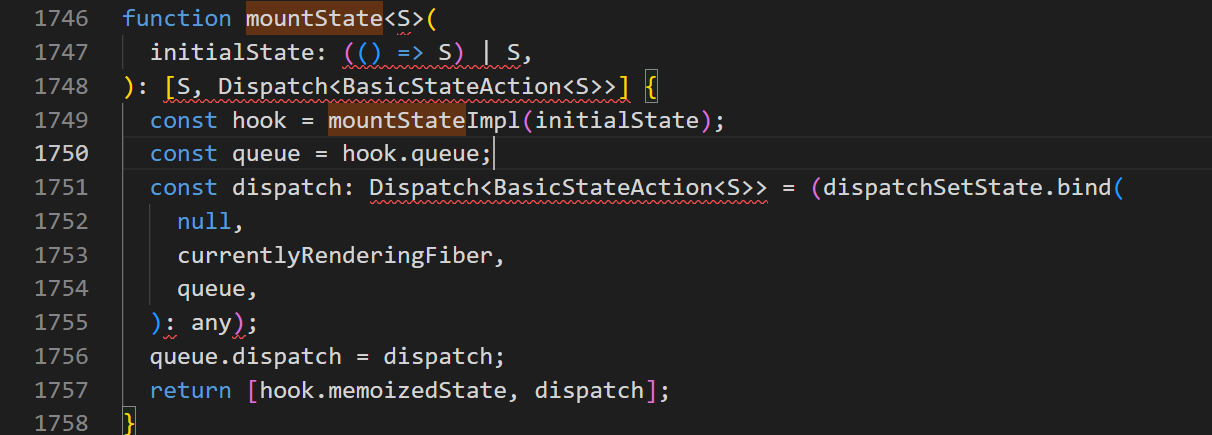 如(三)中所讲:我们在项目中使用useState时const [state, setState] = useState(initialState);
等价于const [state, setState] = mountState(initialState);
那其实根据返回值你就可以知道,你的state和setState其实就分别对应mountState中的hook.memoizedState, dispatch。
所以当我们调用setState时,就是调用的mountState方法中的dispatch变量方法。
那么根据截图中的1751代码行,dispatch方法就是经过bind的dispatchSetState方法。
如(三)中所讲:我们在项目中使用useState时const [state, setState] = useState(initialState);
等价于const [state, setState] = mountState(initialState);
那其实根据返回值你就可以知道,你的state和setState其实就分别对应mountState中的hook.memoizedState, dispatch。
所以当我们调用setState时,就是调用的mountState方法中的dispatch变量方法。
那么根据截图中的1751代码行,dispatch方法就是经过bind的dispatchSetState方法。
五、dispatchSetState
dispatchSetState的实现依旧在packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberHooks.js中。从函数名你也可以看出,dispatchSetState:派发setState。源码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82 function dispatchSetState<S, A>(
fiber: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
action: A,
): void {
if (__DEV__) {
if (typeof arguments[3] === 'function') {
console.error(
"State updates from the useState() and useReducer() Hooks don't support the " +
'second callback argument. To execute a side effect after ' +
'rendering, declare it in the component body with useEffect().',
);
}
}
const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber);
const update: Update<S, A> = {
lane,
revertLane: NoLane,
action,
hasEagerState: false,
eagerState: null,
next: (null: any),
};
if (isRenderPhaseUpdate(fiber)) {
enqueueRenderPhaseUpdate(queue, update);
} else {
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
if (
fiber.lanes === NoLanes &&
(alternate === null || alternate.lanes === NoLanes)
) {
// The queue is currently empty, which means we can eagerly compute the
// next state before entering the render phase. If the new state is the
// same as the current state, we may be able to bail out entirely.
const lastRenderedReducer = queue.lastRenderedReducer;
if (lastRenderedReducer !== null) {
let prevDispatcher;
if (__DEV__) {
prevDispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current;
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
InvalidNestedHooksDispatcherOnUpdateInDEV;
}
try {
const currentState: S = (queue.lastRenderedState: any);
const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action);
// Stash the eagerly computed state, and the reducer used to compute
// it, on the update object. If the reducer hasn't changed by the
// time we enter the render phase, then the eager state can be used
// without calling the reducer again.
update.hasEagerState = true;
update.eagerState = eagerState;
if (is(eagerState, currentState)) {
// Fast path. We can bail out without scheduling React to re-render.
// It's still possible that we'll need to rebase this update later,
// if the component re-renders for a different reason and by that
// time the reducer has changed.
// TODO: Do we still need to entangle transitions in this case?
enqueueConcurrentHookUpdateAndEagerlyBailout(fiber, queue, update);
return;
}
} catch (error) {
// Suppress the error. It will throw again in the render phase.
} finally {
if (__DEV__) {
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = prevDispatcher;
}
}
}
}
const root = enqueueConcurrentHookUpdate(fiber, queue, update, lane);
if (root !== null) {
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(root, fiber, lane);
entangleTransitionUpdate(root, queue, lane);
}
}
markUpdateInDevTools(fiber, lane, action);
}关注我粘贴的这段代码的74~78行。
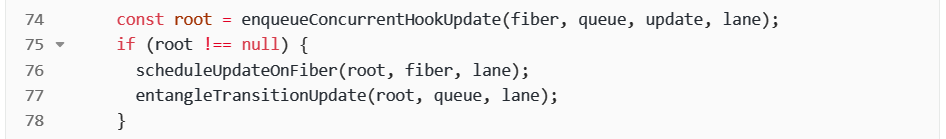 最重要的是第76行:
最重要的是第76行:
 当我们在项目中执行setState时其实就是执行的上述代码,而关键方法就是这个scheduleUpdateOnFiber。
当我们在项目中执行setState时其实就是执行的上述代码,而关键方法就是这个scheduleUpdateOnFiber。
六、scheduleUpdateOnFiber
沿着scheduleUpdateOnFiber->ensureRootIsScheduled->scheduleTaskForRootDuringMicrotask的调用链
在scheduleTaskForRootDuringMicrotask方法的源码实现中,你可以找到如下代码:
 该段代码的含义为创建新任务(performConcurrentWorkOnRoot)将其加入调度器的调度队列中(scheduleCallback()),performConcurrentWorkOnRoot为以Concurrent模式启动渲染fiber的方法。至此setState方法就完成了将任务:以Concurrent模式启动渲染fiber,添加到调度器调度队列中。调度器会在合适的时机调度该任务执行。
该段代码的含义为创建新任务(performConcurrentWorkOnRoot)将其加入调度器的调度队列中(scheduleCallback()),performConcurrentWorkOnRoot为以Concurrent模式启动渲染fiber的方法。至此setState方法就完成了将任务:以Concurrent模式启动渲染fiber,添加到调度器调度队列中。调度器会在合适的时机调度该任务执行。
那么这里就引出了两个概念,调度器和fiber。调度器是指渲染任务的调度机制,fiber你可以认为是虚拟Dom。这两个概念都是一套完整的机制,之后都会细说。